Mobile App Terms and Conditions of Use (Goods)
A Mobile App Terms and Conditions of Use (Goods) outlines the Terms and Conditions of Use for a mobile application.
Last updated October 23, 2025
Suitable for Australia
Create & Customise Legal Templates Online
What is a mobile app terms and conditions of use (goods)?
What is a mobile app terms and conditions of use (goods)?

When should you use a mobile app terms and conditions of use (goods)?
When should you use a mobile app terms and conditions of use (goods)?
What should be in a mobile app terms and conditions of use (goods)?
What should be in a mobile app terms and conditions of use (goods)?
How to create a legal document
- check_circle
Access the Document Library
- check_circle
Select the template that matches your needs
- check_circle
Customise by adding or removing clauses with assistance from Lawpath AI
- check_circle
Personalise with your headers, footers, logos, or additional text
- check_circle
Store all documents securely in your account for easy access
Frequently asked questions
How does this document protect my app and business?
keyboard_arrow_upWhat limitations does this document place on users?
keyboard_arrow_upDoes this document cover privacy requirements?
keyboard_arrow_upIs this document suitable for all Australian states and territories?
keyboard_arrow_upWhat are the risks of using this document?
keyboard_arrow_upHow can I make these terms legally binding for my app users?
keyboard_arrow_upDo I need to update these terms regularly?
keyboard_arrow_upView Sample Mobile App Terms and Conditions of Use (Goods)
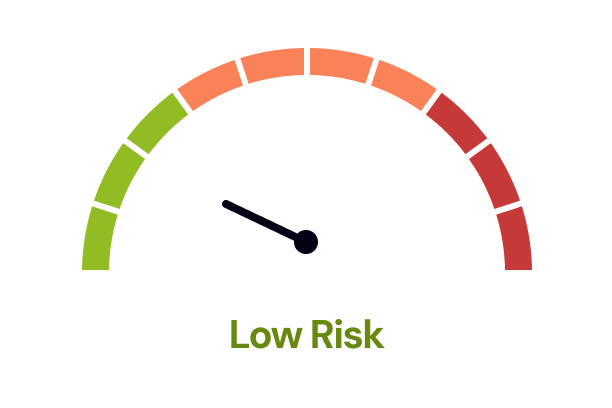
The Legal Risk Score of a Mobile App Terms and Conditions of Use (Goods) Template is Low
Our legal team have marked this document as low risk considering:
- Users may find themselves bound by changes to the terms and conditions without prior agreement, as the operator reserves the right to modify terms at any time and only promises to attempt to notify users of these changes.
- There is a limitation on the user's ability to claim for indirect or consequential losses, which might not fully compensate the user for all potential damages experienced due to issues with the purchase services or products.
- The document specifies that any legal disputes must be handled exclusively in the courts of a specific location, potentially disadvantaging users who are based in other regions or countries due to travel and legal representation costs.
Overall, this document places a significant amount of control in the hands of the operator, including the ability to change terms and limit liabilities, which could present higher risks for users compared to more balanced agreements. Users familiar with such documents might understand the typical risks involved but should consider whether the specific limitations and obligations outlined align with their personal or business risk tolerance.
Meet Our Users
Articles about Mobile App Terms and Conditions of Use (Goods)
Looking for more documents?
Privacy Policy
A Privacy Policy outlines how your business will use, store and collect your customers' information. A Privacy Policy is required by law in certain circumstances.
Website Terms and Conditions of Use (Services)
This Website Terms and Conditions of Use (Services) document is specifically tailored for websites selling services.
Website Disclaimer (General)
A Website Disclaimer (General) provides notice to the visitor of the website and is used to limit liability for legal issues that may arise when a user visits the website.
Confidentiality Agreement (Mutual)
This Confidentiality Agreement (Mutual) allows you and another party to share confidential information while legally forbidding the other party from disclosing that information to any other person or entity.
GDPR Privacy Policy
This Privacy Policy variation is created specifically for websites to abide by the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) framework from the European Union (EU).
Website Terms and Conditions of Use (Goods)
This Website Terms And Conditions of Use (Goods) outlines the rules people must follow when using your website. It includes protection for your IP, disclaimers to limit your liability and makes you compliant with Australian law.
Licensing Agreement (IP)
A Licensing Agreement (IP) is a legal document that enables a company to grant the use of its intellectual property to another business.
Information Security Policy
An Information Security Policy outlines the management of information within your business.